Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as a cornerstone in treating mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, and insomnia. As a structured, goal-oriented therapy, CBT focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to emotional distress. In this blog, we will delve into how CBT effectively addresses these common mental health struggles, helping individuals lead healthier, more balanced lives.
What is CBT?
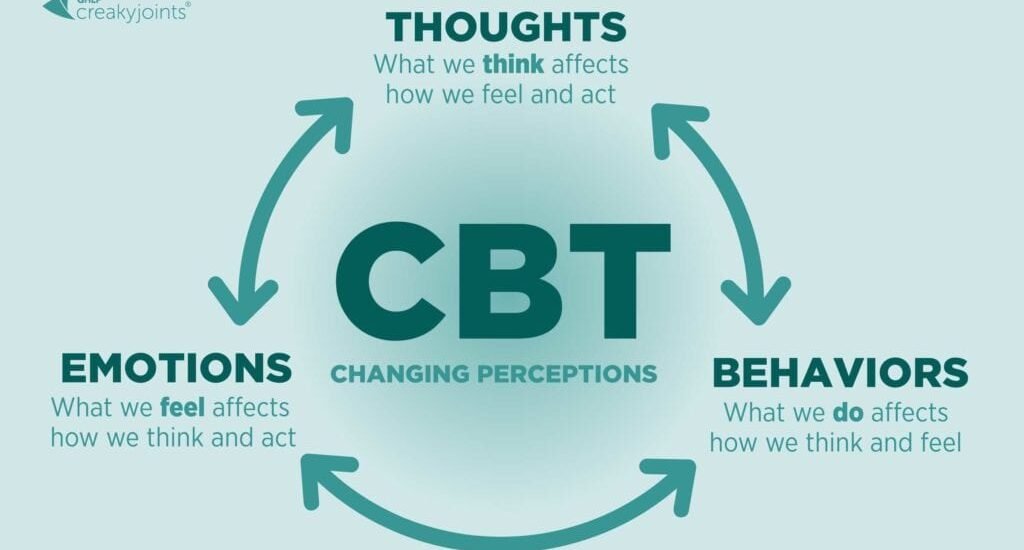
At its core, CBT is a type of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors. By recognizing distorted thinking and learning new coping strategies, patients can better manage their emotions and improve their mental health. CBT is a collaborative process, with the therapist and patient working together to set goals and develop practical skills for managing symptoms.
CBT for Anxiety
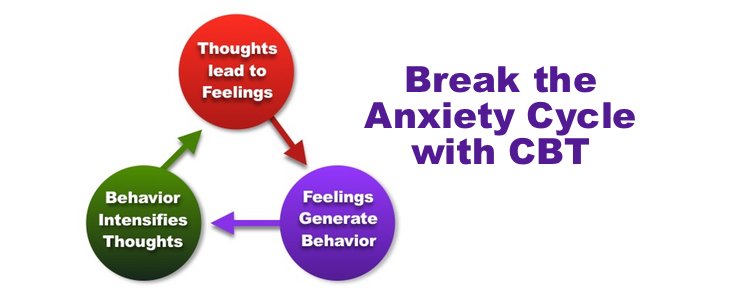
Anxiety is often rooted in irrational fears or worries about future events. These fears can lead to avoidance behaviors, which, in turn, perpetuate feelings of anxiety. CBT helps individuals with anxiety by:
- Identifying and challenging negative thoughts: People with anxiety often experience catastrophic thinking, believing that the worst-case scenario will occur. CBT helps individuals recognize these distorted thoughts and replace them with more realistic perspectives.
- Exposure therapy: Gradually confronting feared situations or triggers in a controlled manner can reduce avoidance behavior and desensitize individuals to their anxieties.
- Relaxation techniques: CBT also incorporates relaxation exercises, such as deep breathing, to reduce the physiological symptoms of anxiety, including rapid heart rate and shallow breathing.
Studies have shown that CBT is effective in treating a wide range of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety, and panic disorder
Drug Discovery and Development
CBT for Depression
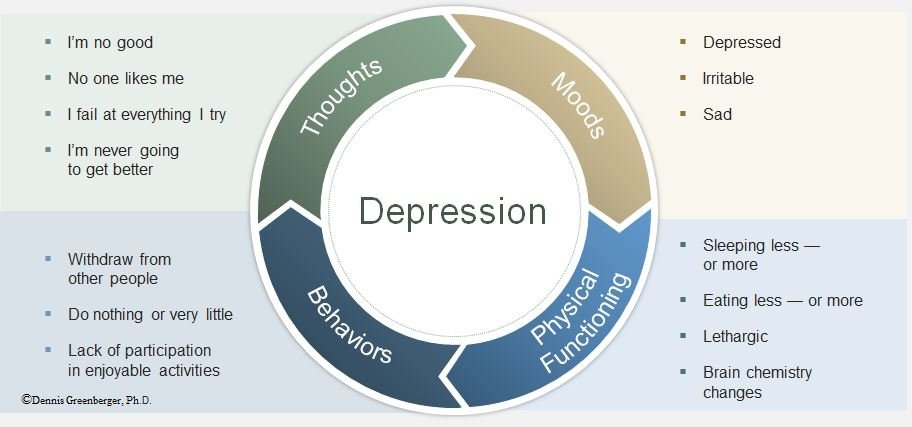
Depression is often accompanied by negative self-talk and a distorted view of the world. CBT helps individuals by:
- Identifying cognitive distortions: Depressed individuals may engage in black-and-white thinking, overgeneralizing negative experiences. CBT helps identify these cognitive distortions and teaches individuals to challenge them.
- Behavioral activation: Depression can lead to inactivity and withdrawal from pleasurable activities. CBT encourages individuals to engage in rewarding activities, even if they don’t initially feel like it. This helps break the cycle of withdrawal and enhances mood over time.
- Building problem-solving skills: CBT teaches individuals to cope with difficult situations in a more balanced and effective way, reducing the feelings of helplessness often associated with depression.
Research consistently shows that CBT is an effective treatment for depression, often achieving results comparable to medication for many individuals
Drug Discovery and Development
.
CBT for Insomnia

Insomnia is often linked to anxiety and depression, but it can also exist independently as a sleep disorder. CBT for insomnia (CBT-I) focuses on changing behaviors and thoughts that interfere with sleep. Key components include:
- Stimulus control: This involves associating the bed and bedroom only with sleep, thereby breaking the cycle of anxiety and restlessness that can develop in the bedroom.
- Sleep restriction: Limiting time in bed to the actual time spent sleeping can help consolidate sleep and reduce fragmented sleep patterns.
- Cognitive restructuring: Negative thoughts about sleep, such as worrying about not being able to fall asleep, can create a self-fulfilling prophecy. CBT-I helps individuals replace these thoughts with more constructive ones, promoting a sense of control over their sleep.
CBT-I has been shown to be highly effective for individuals with chronic insomnia, improving sleep quality and duration
Drug Discovery and Development
The Benefits of CBT
CBT is considered one of the most evidence-based therapies available for anxiety, depression, and insomnia. The key benefits include:
- Long-lasting results: CBT equips individuals with skills they can use throughout their lives. Unlike medications, which may require ongoing use, CBT helps individuals manage their symptoms independently once treatment is complete.
- Practical and structured: CBT provides a clear, structured approach to solving mental health problems, which can be empowering for patients.
- Minimal side effects: Unlike medications, CBT has few, if any, side effects, making it a safe option for many people.
Conclusion
Cognitive behavioral therapy has proven to be an effective and versatile treatment for anxiety, depression, and insomnia. By targeting the root causes of these conditions—negative thoughts and unhelpful behaviors—CBT empowers individuals to take control of their mental health and lead more fulfilling lives. Whether used alone or in conjunction with medication, CBT can provide lasting relief for those struggling with these common mental health challenges.
If you’re interested in exploring CBT further or finding a therapist near you, consider reaching out to a licensed professional trained in CBT techniques.