Supporting Mental Health: The Role of Antidepressants in Stress-Free Living
In a world where stress has become a pervasive challenge, many individuals find themselves struggling to manage the emotional and physical impacts of stress. While lifestyle changes, stress-reduction techniques, and therapy are essential for long-term mental health, antidepressants play a significant role in helping individuals cope with chronic stress and mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression. This blog post explores the role of antidepressants in promoting stress-free living, their benefits, potential risks, and the importance of a comprehensive treatment plan.
What Are Antidepressants?
Antidepressants are medications prescribed to treat depression and anxiety disorders, but they can also be effective in managing symptoms of chronic stress. These medications work by altering the balance of certain neurotransmitters in the brain—chemicals that help regulate mood, emotions, and stress responses. The most commonly prescribed antidepressants are part of a class of drugs known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
How Antidepressants Help Manage Stress
Chronic stress can be a trigger for mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. Over time, stress can deplete important neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, leading to feelings of hopelessness, irritability, or even physical symptoms like headaches and fatigue. Antidepressants help restore the balance of these neurotransmitters, improving mood, reducing anxiety, and stabilizing the body’s stress response. Here’s how antidepressants help manage stress:
1. Restoring Chemical Imbalance
The brain’s neurotransmitters are responsible for regulating mood and stress. In individuals experiencing chronic stress, the serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine systems can become unbalanced. Antidepressants help restore these chemicals, allowing individuals to regain a sense of stability, calm, and resilience when faced with stressful situations.
2. Reducing Symptoms of Anxiety
Stress often manifests as anxiety, which can lead to a cycle of worry, nervousness, and physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and muscle tension. Antidepressants, particularly SSRIs and SNRIs, are often prescribed to manage anxiety. These medications help calm the brain’s overactive stress response and improve emotional regulation, making it easier to cope with daily stressors.
3. Improving Sleep
Stress can often lead to sleep disturbances, including insomnia, making it difficult to relax and recover from the day’s challenges. Some antidepressants, especially tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) like amitriptyline, can have sedative effects, improving sleep quality and allowing individuals to rest and recharge. Better sleep enhances emotional well-being and resilience, making it easier to manage stress during waking hours.
4. Enhancing Emotional Regulation
Chronic stress can overwhelm emotional control, causing individuals to feel out of touch with their feelings or unable to manage emotional ups and downs. Antidepressants help to regulate mood and emotional responses, allowing individuals to navigate stressful situations with greater calm and confidence. This makes it easier to maintain a positive outlook, even during challenging times.
Types of Antidepressants Used to Manage Stress
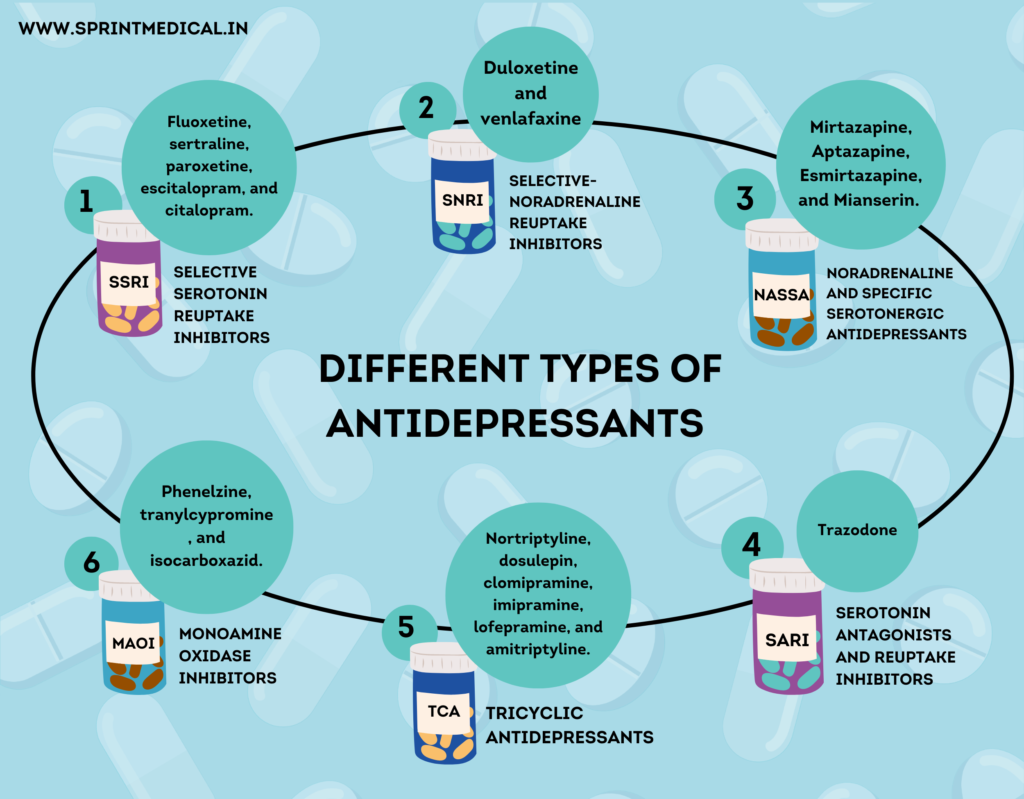
Different types of antidepressants are prescribed based on the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and response to treatment. Below are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants for stress and anxiety relief:
1. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Examples: Fluoxetine (Prozac), Sertraline (Zoloft), Citalopram (Celexa), Escitalopram (Lexapro)
- How they work: SSRIs work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, allowing more serotonin to be available to improve mood and reduce anxiety.
- Uses: SSRIs are commonly prescribed for generalized anxiety disorder, depression, and panic attacks.
2. Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Examples: Venlafaxine (Effexor), Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- How they work: SNRIs increase the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine, chemicals that regulate mood and stress. By targeting both neurotransmitters, SNRIs are effective in treating anxiety, depression, and physical symptoms of stress like fatigue and pain.
- Uses: SNRIs are effective for both anxiety and chronic stress, as well as pain relief in conditions like fibromyalgia and chronic back pain.
3. Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
- Examples: Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- How they work: TCAs affect several neurotransmitters, including serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine. These medications have sedative effects, which can help individuals relax and improve sleep.
- Uses: TCAs are generally prescribed for depression, chronic pain, and insomnia, though they are less commonly used now due to their side effect profile.
4. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Examples: Phenelzine (Nardil), Tranylcypromine (Parnate)
- How they work: MAOIs work by blocking the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the brain. This results in higher levels of these neurotransmitters, which can improve mood and reduce anxiety.
- Uses: MAOIs are used for severe cases of depression and anxiety, particularly when other medications are ineffective.
Benefits of Antidepressants for Stress-Free Living
- Improved Mood: Antidepressants can help improve overall mood, making it easier to approach daily tasks and challenges with a more positive mindset.
- Increased Resilience: By stabilizing mood and improving emotional regulation, antidepressants help individuals become more resilient to stress, allowing them to bounce back from setbacks with greater ease.
- Better Sleep: Improved sleep quality allows individuals to recover from daily stress and feel refreshed and energized.
- Reduced Anxiety: By managing anxiety, antidepressants can help individuals feel calmer and more focused, enabling them to handle stress more effectively.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While antidepressants offer significant benefits for managing stress, they are not without their risks:
- Side Effects: Some individuals may experience side effects, including weight gain, sexual dysfunction, dry mouth, or nausea. It may take time to find the right medication and dosage.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Stopping antidepressants suddenly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including dizziness, irritability, and headaches. It’s important to taper off these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Delayed Onset: Antidepressants typically take several weeks to start showing their full effects, so individuals may not experience immediate relief from stress.
When to Seek Professional Help
Antidepressants can be a helpful part of a broader stress management plan, but they should be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional. It’s essential to have a comprehensive treatment plan that includes therapy, lifestyle changes (such as regular exercise and a healthy diet), and stress-reduction techniques to achieve the best results. If you’re feeling overwhelmed by stress, anxiety, or depression, seeking professional guidance is the first step toward finding the right treatment for your needs.

Conclusion
Antidepressants can play a vital role in supporting mental health and fostering stress-free living. By restoring neurotransmitter balance, improving emotional regulation, and reducing symptoms of anxiety, these medications offer relief to those struggling with chronic stress. However, they should be used as part of a holistic approach to stress management, which may include therapy, lifestyle changes, and coping strategies. By working with a healthcare provider, individuals can find the right treatment plan to manage stress and improve overall well-being.